Big Tech on Trial: A Systematic Review of Class Action Lawsuits

Litigation against big-tech companies began with high-profile US government antitrust cases, like those against IBM (1969), AT&T (1974), and Microsoft (1998). But has since expanded to include consumer led class actions against companies like Apple, Adobe, Intel, and Google, often related to data privacy and security.
The ability these companies now have to gather and use personal information, and to use that data to corner a market, is unprecedented. The rise in lawsuits and regulations can be seen not only in the US, but also in the EU, UK, Australia, and India. This reflects increasing user efforts to hold companies accountable for how they handle data and ensure fair market practices.
However, are rising public distrust, stricter regulations, and more frequent litigation helping to create accountability? Or are they simply becoming a cost of doing business?
In this article, our research team at vpnMentor examines whether billion-dollar lawsuits are truly holding tech firms accountable, or if they’re simply reshaping their business strategies. We analyzed a random sample of 79 major class action lawsuits from the past five years to highlight emerging trends. We look at their legal and financial consequences, as well as the implications for consumers, AI ethics, and future tech regulations.
The Rise of Tech-Related Class Action Lawsuits
Tech companies are increasingly facing legal challenges from both private entities and government bodies through class action lawsuits, escalating across three major categories:
- AI-Driven Privacy Lawsuits: Legal challenges targeting AI systems for unauthorized personal data collections and decision-making biases.
- Privacy Violation Lawsuits: Lawsuits addressing data breaches, unauthorized tracking, and improper data sharing.
- Tech Product Recall Lawsuits: Lawsuits involving defective or unsafe technology products that put consumers at risk.
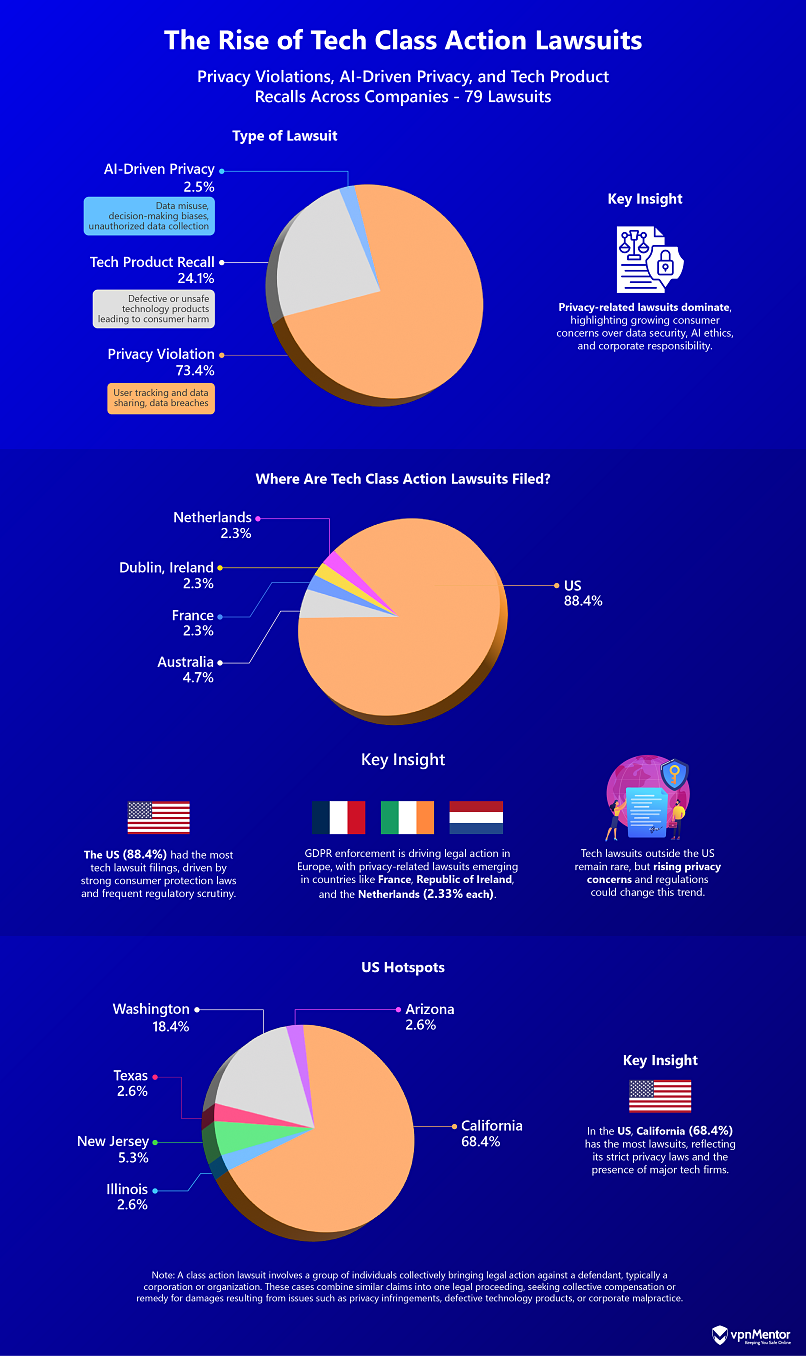
The majority of class action lawsuits in our data set (79 cases) are privacy related (58 cases), highlighting growing public concerns over data handling and security, AI-driven decision-making, and corporate responsibility.
The preceding graphic also highlights rising global concerns regarding privacy, with most tech-related class action lawsuits (88.4%) happening in the US. States like California, Illinois, and Washington, which have strong consumer protection laws (e.g., CCPA, BIPA), have become key battlegrounds for cases involving AI-driven privacy violations, data misuse, and product liability.
Beyond the US, GDPR enforcement is driving privacy lawsuits in Europe, with emerging cases in France, the Netherlands, and Ireland. While large-scale class action suits outside the US remain rare, the increasing focus on data privacy and security could shift this trend.
Privacy Lawsuits: Key Settlements (2015-2025)
As technology becomes increasingly integrated into daily life, concerns over data privacy and security have increased, particularly with the rise in data breaches and unauthorized data sharing for the purposes of marketing and sales.
In the past five years, privacy-related lawsuits have surged, with major tech and non-tech companies facing substantial damages and settlement payouts for unauthorized data collection, biometric privacy violations, and large-scale data breaches.
Notable companies like Apple, Alphabet (Google), Meta, and Samsung have faced significant regulatory fines and class action lawsuits over privacy and data security issues, with damages reaching hundreds of millions of dollars (USD).
Many cases against tech giants arise from government actions for issues like unauthorized user tracking, security flaws, and violations of children’s privacy laws. But private individuals have also filed class action lawsuits, leading to some settlements, ongoing cases, and a few dismissals.
This section explores some of the major privacy-related lawsuit settlements, emphasizing the key privacy concerns fueling these legal actions.

Unauthorized data collection and mishandling of sensitive information have led to significant privacy risks. Companies like Samsung have faced lawsuits under the Illinois BIPA for collecting biometric data, such as facial and voice recognition, without user consent. Additionally, data breaches have exposed millions to privacy risks, with Ally Financial (4.2M users) and loanDepot (16.9M users) facing civil suits for mishandling sensitive information.
These unauthorized data collection and security breaches show the need for increased protections and controls around data security and privacy. While the US remains the epicenter of privacy lawsuits (88%), countries like Australia, France, Ireland, and the Netherlands (4% each) are also tightening privacy regulations to protect consumers from tech-related risks.
Out of 58 related cases, 15 have been settled, while 43 remain ongoing, highlighting the growing role of privacy lawsuits in shaping digital rights and corporate accountability, worldwide.
The AI Lawsuit Wave: Users Fight Back Against Data Scraping
AI-powered technologies have sparked a wave of lawsuits. The benefits of being able to harvest and process data are vast, and companies appear to be willing to skirt laws and regulations in order to access this valuable resource.
Companies are known to collect the personal data of their user base and copyrighted data of the public at-large, often without informed consent. This data is used to train base models, to tune models for applications, and to better market and develop products, among other uses.
Plaintiffs in these class action suits include individuals and groups of users alleging privacy violations, as well as artists, musicians, writers, and other content creators accusing companies of copyright infringement. Additionally, federal authorities, media outlets, and publishing houses have also filed lawsuits related to various legal violations.
These plaintiffs are primarily challenging companies’ practices regarding data scraping, surveillance, algorithmic bias, and unauthorized use of copyrighted work in AI model training and outputs.
The 2022 lawsuit filed against Tesla for its Autopilot feature was one of the earliest cases filed against a big-tech company for its practices around AI. By 2023, a major lawsuit against Google (Alphabet) was filed for data scraping and AI-powered ad tracking, followed by similar cases against Meta and YouTube regarding AI model training on copyrighted content.
The graph below highlights notable AI-related lawsuits and the oversight of AI-driven data collection, emphasizing the desire from users and other interested parties to hold companies accountable for their alleged practices.
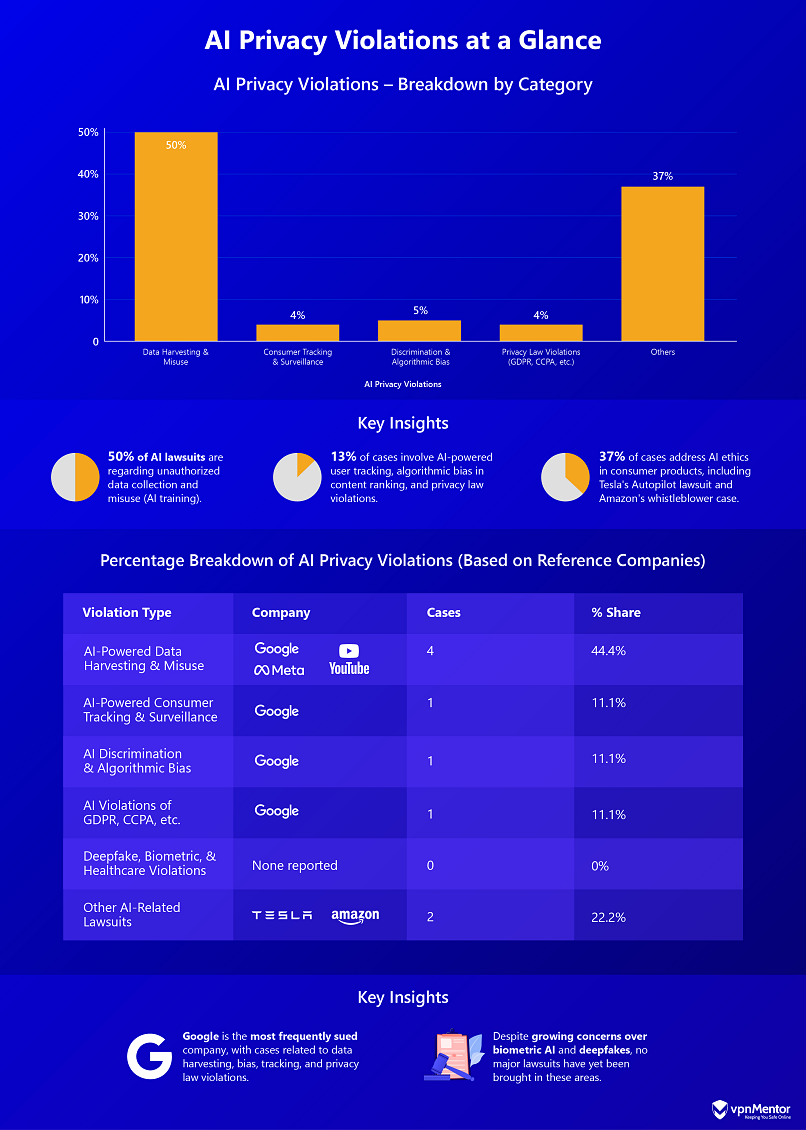
Tech giants like Alphabet and Meta (37.5% respectively) are among the most common defendants in cases involving AI-driven privacy violations, while Amazon and Tesla (12.5% respectively) have faced legal challenges for issues ranging from unauthorized data use to misleading claims about AI-powered products. These cases highlight the growing concerns about ethical use of AI and privacy in the tech industry.
Geographically, the majority (88%) of AI-related lawsuits have been filed in the US. This is largely due to its strong consumer protection laws and relatively large population, as well as the fact that many tech companies are headquartered in the US.
As legal battles intensify, the future of data governance and the digital rights of users will be shaped by AI regulations and corporate accountability. For instance, Colorado is the first US state to regulate AI, with new requirements for high-risk AI systems set to take effect in 2026, aiming to prevent consumer harm and discrimination.
In 2024, the EU approved the Artificial Intelligence Act, which adopts a risk-based approach that imposes stricter regulations on higher-risk AI systems. Meanwhile, Japan is considering requiring major AI developers to disclose information for security and fairness.
Tech Recalls & Product Safety: A Growing Concern in Consumer Protection
Tech-related product recalls have increased across industries, highlighting significant safety risks linked to defective components. Companies like Honda, BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, Whirlpool, and Electrolux have all faced lawsuits for products ranging from automobiles to home appliances that present serious hazards to consumers.
Many of these companies have faced class action lawsuits for failing to act swiftly, despite being aware of the defects, leaving consumers exposed to potential danger and financial losses.
The graph below highlights significant tech recalls and product safety issues, reflecting increased public awareness and the ongoing debate about the need for stronger proactive measures to ensure accountability before problems occur.
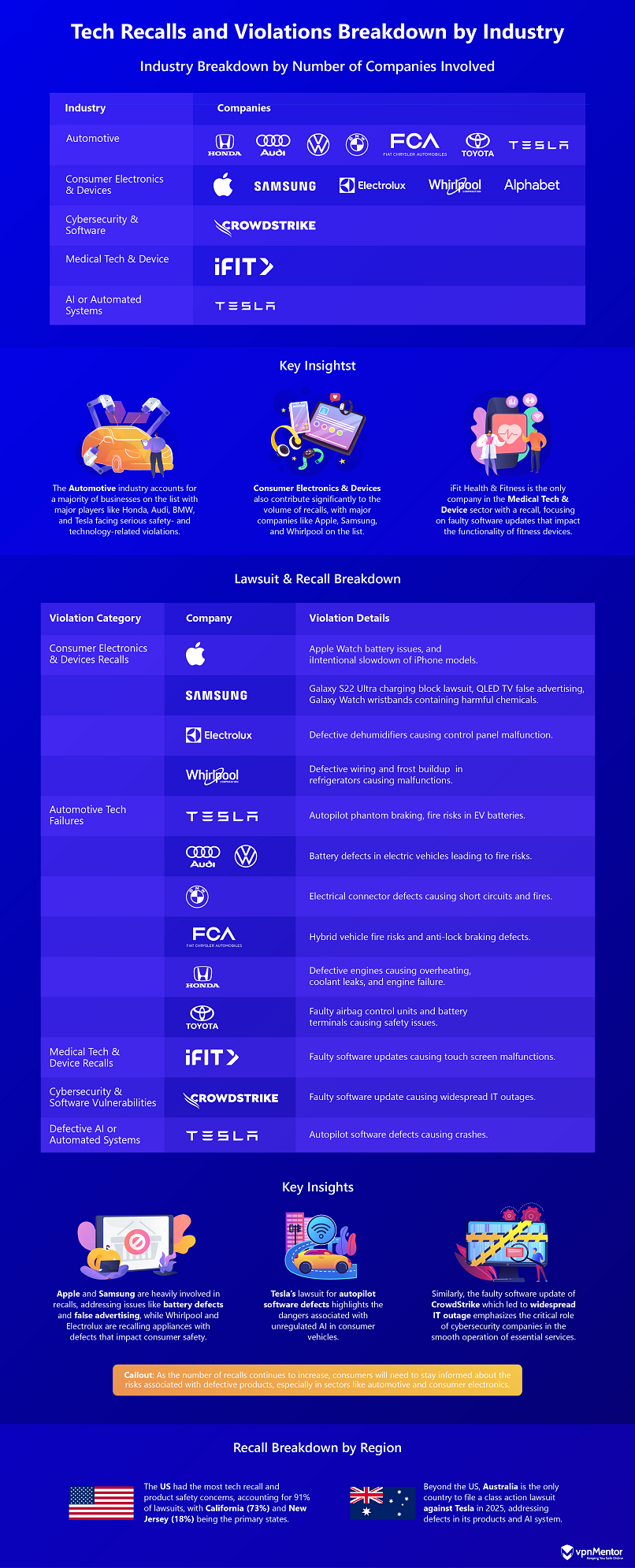
These widespread legal challenges highlight the growing concerns over product safety and corporate responsibility. As lawsuits continue to rise, companies are facing pressure to address defects and ensure consumer safety. The rise of modern communication channels has amplified these concerns, making it harder for companies to resolve issues with compensation alone.
The breakdown of lawsuits and recalls, particularly in 2024, reveals significant concerns across industries, especially in automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices. Tesla, for example, is involved in multiple incidents, including autopilot malfunctions and fire risks in electric vehicle batteries, while consumer electronics giants like Samsung face recalls over safety and performance issues.
Trends in Class Action Lawsuits: Insights From Tech-Related Companies
The increasing frequency of lawsuits in tech-related industries highlights growing concerns over privacy violations, AI-driven issues, and product safety. Companies like Microsoft, Samsung, and Tesla are struggling with class-action lawsuits and product recalls.
Below is a detailed look at the litigation landscape for some of the industry’s leading players between 2018 and 2025.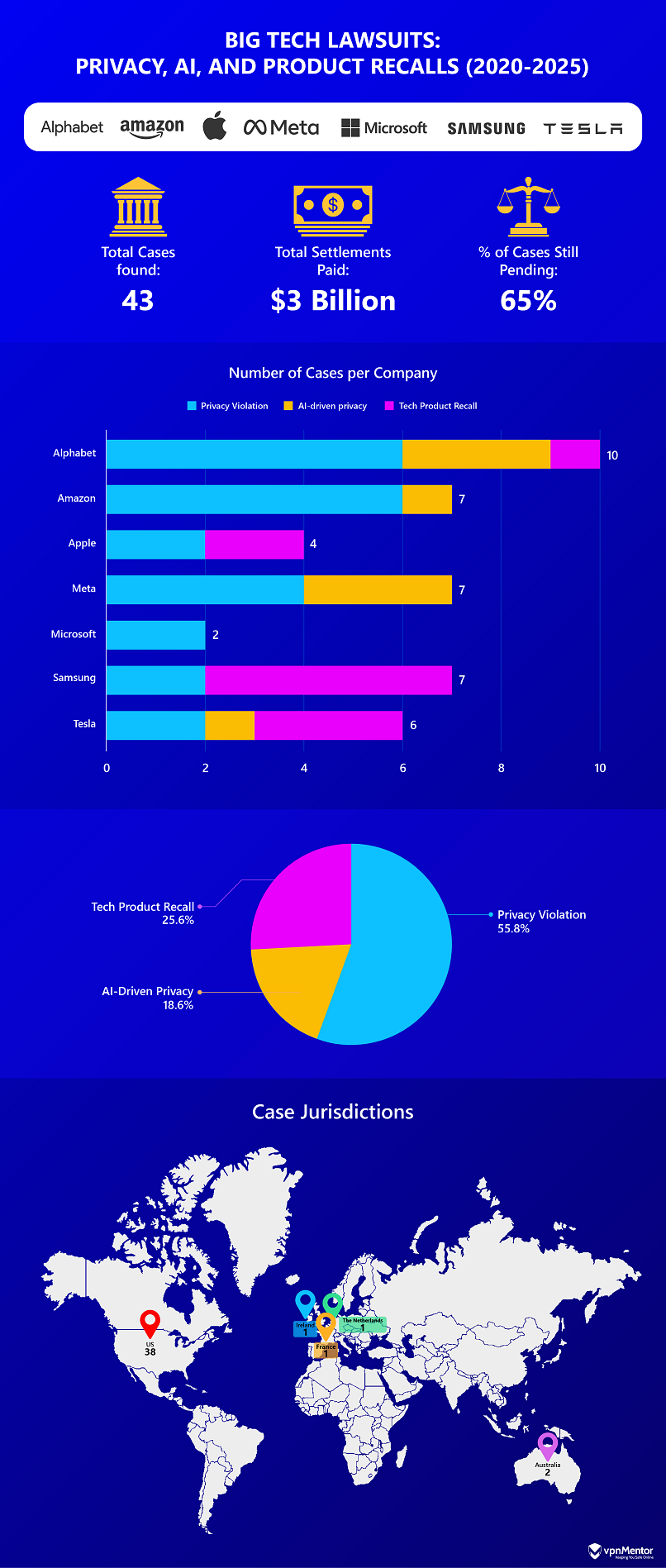
Big tech companies have faced 43 lawsuits since 2018, with Alphabet leading at 10 cases. Privacy violations are the most common (55.8%), followed by tech product recalls (25.6%) and AI-driven privacy concerns (18.6%).
Despite $3 billion in settlements, 65% of cases are still ongoing, highlighting the increasing legal attention on data privacy and product safety in the tech industry.
Number of Cases Filed: Breakdown by Category (2018-2025)
Lawsuit Filing Trend (2018–2025)
Lawsuit Settlement Trend (2020–2025)
Lawsuits Not Yet Settled

Between 2020 and 2025, Alphabet and Amazon had the most class action lawsuits filed against them, with privacy violations being the most common issue, particularly for Amazon (86%) and Microsoft (100%). AI-driven privacy concerns were notable for Alphabet, Meta, and Tesla, while Samsung and Tesla faced the highest proportion of tech product recall cases.
Despite significant lawsuit activity, settlements remained low, with many cases still unresolved. At the time this article was published, Amazon had all seven cases pending, and Tesla had 83% unsettled. In contrast, Apple, Alphabet, and Meta bore the greatest financial impact, with Meta paying the highest settlement at $1 billion.
California emerged as the primary litigation hub, particularly for Alphabet, Apple, and Meta, while Amazon faced all seven lawsuits in Washington, where it is headquartered.
These trends highlight the increasing financial and legal risks for tech giants as regulatory scrutiny intensifies worldwide.
Accountability? Or Just a Cost of Doing Business?
Despite billions in settlements from class action lawsuits, including 75 million USD by Meta and the 100 million USD by Apple, many companies continue to face similar allegations, from privacy violations to defective products.
Meta, for instance, has faced multiple lawsuits over unauthorized data use and remains under regulatory scrutiny. In May 2025, Apple was hit with another class-action lawsuit for allegedly violating a 2021 antitrust injunction, despite losing the said iOS developer lawsuit.
Meanwhile, Samsung has been frequently sued under Illinois’ BIPA for biometric data violations, while Tesla has faced litigation and recalls related to autopilot malfunctions.
These recurring legal challenges and product issues suggest that financial penalties alone have not led to behavioural or operational changes among major tech firms across different sectors.
With 65% of class action cases still ongoing, a critical question rises — are these lawsuits creating real accountability, or are they just another operational cost for these large firms?
Despite large payouts, the majority of these companies continue to be riddled by legal challenges, suggesting that settlements may function more as damage control than deterrents.
While new regulations like Colorado’s upcoming AI law and the EU’s AI Act signal a push for proactive regulation, their true impact will depend on how well these regulations are enforced and the extent to which they drive meaningful changes in corporate practices.
Methodology
This article examines class action lawsuits against major technology companies, focusing on privacy violations, AI-related disputes, and technology product recalls. It aims to identify trends, legal outcomes, and industry impact by analyzing publicly available cases from 2015 and 2025.
Data was sourced from ClassAction.org, Consumer Action, Top Class Actions, regulatory filings (FTC, SEC, EU regulators), and media outlets like Reuters and The Verge. A random sample of 58 cases was selected to provide a snapshot rather than a comprehensive dataset. Cases were categorized into:
- Privacy Violations – Data misuse, unauthorized tracking, and user privacy breaches.
- AI-Driven Privacy Lawsuits – Legal actions related to AI misuse in data collection and content generation.
- Tech Product Recalls – Class actions involving defective or hazardous technology products.
The study assessed lawsuit frequency, legal consequences, and financial impacts. Companies were selected based on market capitalization, revenue, global reach, and influence in AI, cloud computing, and consumer electronics. Data collected included company name, lawsuit type, filing year, legal outcome, and settlement amount (if applicable).
Limitations include restricted access to confidential lawsuit settlements, ongoing cases without final resolutions, and regional legal differences affecting comparisons.
This methodology provides a structured framework to understanding Big Tech’s legal battles and their implications for corporate accountability, financial impacts, and regulatory trends.
Discussion
In conclusion, the surge in class action suits against tech and non-tech companies underscores the growing push for corporate accountability in privacy, AI ethics, and product safety.
While legal battles have led to multi-billion-dollar settlements, many cases are still pending, highlighting the challenges in resolving disputes and stopping harmful practices in tech industries.
As regulatory scrutiny intensifies worldwide, the long-term impact of these legal actions on industry practices remains to be seen.
React to this headline: