What Is a WiFi Hotspot and How Does It Work: A Simple Guide
Imagine you’re out and about — at a cafe, in the airport, or sitting in a park — and you want to connect to the internet. That’s where a WiFi hotspot comes to the rescue. It lets you access the web on your devices without needing a wired connection or using up your mobile data. But what exactly is a WiFi hotspot, and how does it work?
In this guide, I’ll break it all down into easy-to-understand terms with no confusing tech jargon. Whether you’re curious about how WiFi hotspots work, the different types of hotspots, or tips to stay safe while using one, I’ve got you covered. Let’s get started!
What Is a WiFi Hotspot?
A WiFi hotspot is a wireless access point that allows you to connect your devices — like smartphones, laptops, or tablets — to the internet. Think of it as a bridge between your device and the web.
Hotspots can be created with mobile phones, a dedicated hotspot device, or public WiFi routers. When you’re near a hotspot, you can join its network just like you would with your home WiFi.
WiFi Hotspot Terminology
Understanding WiFi hotspots is easier when you’re familiar with the terms commonly used around them. Here’s a straightforward explanation of the most important terms:
- WiFi. This is the technology that allows devices to connect wirelessly to a network. It uses radio waves to transmit data, eliminating the need for physical cables. WiFi powers your home internet, public hotspots, and even mobile hotspots.
- Hotspot. A hotspot is any physical location or device that provides wireless internet access. Think of it as the “WiFi zone” you connect to.
- Access point (wireless access point). An access point (AP) is a device, like a router, that creates a wireless network for devices to join. In the context of WiFi hotspots, it’s the hardware that generates the WiFi signal, allowing you to connect to the internet wirelessly.
- SSID (service set identifier). The SSID is the name of a WiFi network. When you search for available networks on your phone or laptop, the names you see (like CoffeeShop_WiFi or HomeNetwork123) are SSIDs. It’s basically the label that helps you identify which WiFi network to join.
- Tethering. Tethering is the process of sharing your phone’s internet connection with another device, like a laptop or tablet. This can be done in three ways: via WiFi (mobile hotspot), USB cable (USB tethering), or Bluetooth.
- USB tether/USB modem. USB tethering is a type of tethering where you connect your phone to another device using a USB cable. It’s often more stable than WiFi tethering because it doesn’t rely on wireless signals. Some phones even refer to this feature as the USB modem.
- Bluetooth tethering. This method uses Bluetooth to share your phone’s internet connection. It’s slower than WiFi or USB tethering but can be helpful if you want to conserve your phone’s battery.
- Modem. This is the device that connects your network to the internet. It pulls the signal from your internet service provider (ISP) and makes it available for use. Without a modem, there’s no internet to share.
- Router. A router, on the other hand, is a device that distributes the internet connection to your devices wirelessly (or through cables) and creates the WiFi network you connect to. In a WiFi hotspot setup — whether at home, in a cafe, or on your phone — the router generates the WiFi signal that your devices join.
Types of WiFi Hotspots
WiFi hotspots come in different forms, each suited to specific needs. Let’s take a look at the most common types and how they’re used:
1. Public WiFi Hotspots
These are the WiFi networks you find in coffee shops, hotels, airports, and other public spaces. They’re usually free (or sometimes require a small fee) and are super convenient when you’re out and about. But keep in mind, since lots of people use them, they can be slower — and not always the safest option for your personal data.
2. Mobile Hotspots
Mobile hotspots let you share your phone’s cellular data to create a WiFi connection. Most smartphones have this feature built-in, making it easy to connect devices like laptops or tablets when you’re away from regular WiFi. It’s super handy for quick internet access, but heavy usage can quickly eat up your mobile data.
Unlimited data plans can be an excellent option for those who frequently rely on mobile internet. Just watch out for fair usage policies, which might reduce speeds after you hit a specific data limit.
3. Private Hotspots
These are the secure WiFi networks you set up at home or in the office using a router or modem. They’re not portable, but they offer fast, reliable internet for all your devices. Plus, since you control who connects, your network stays safe and speedy.
4. Subscription-Based Hotspots
Some internet providers offer hotspot networks as part of their plans. These hotspots are strategically located in public places like cafes, parks, and airports, and they let you connect to hotspots while on the move. Think of them as an extension of your home WiFi, but nationwide. They’re often faster and more secure than public WiFi, making them a solid choice if you’re always traveling.
5. Portable Hotspot Device
Portable hotspot devices are small, pocket-sized gadgets designed to provide internet access on the go. They use a SIM card to connect to cellular networks and create a WiFi hotspot that multiple devices can join.
These devices are ideal for digital nomads, travelers, or anyone who needs a dedicated, reliable internet connection. Models like the NETGEAR Nighthawk M6 or Huawei E5577 offer excellent speed and coverage, making them a dependable choice for frequent users.
How WiFi Hotspot Works
WiFi hotspots create a wireless network that allows nearby devices to connect to the internet. Mobile hotspots, specifically, use cellular data from providers (like 4G LTE or 5G networks) to generate a WiFi signal. Once a hotspot is turned on, nearby devices can connect to it just like they would to any other WiFi network.
The signal strength and speed can weaken with distance. Most mobile hotspots work best within a range of 10-15 meters (about 30-50 feet), ensuring a reliable connection when you’re close by.
It’s important to remember that mobile and portable hotspots rely on cellular service to function. Without a cell signal or an active data plan, they can’t create a WiFi network. Whether you’re using a smartphone, a dedicated hotspot device, or a portable gadget, the cellular network serves as the bridge between your devices and the internet.
However, public hotspots, like those in cafes or libraries, operate differently. They typically use a wired internet connection, such as DSL or fiber, to create the WiFi network. These don’t depend on cellular service, so they’re accessible to anyone within the network’s range.
How to Turn On a WiFi Hotspot?
Turning your device into a WiFi hotspot allows you to share your internet connection with other devices. Here’s how to set it up:
1. How to Turn On a WiFi Hotspot on a Laptop (Windows or Mac)
Windows
- Open Settings and navigate to Network & Internet > Mobile Hotspot. Toggle on Share my Internet connection with other devices. Select the internet source you want to share (Ethernet or Wi-Fi).
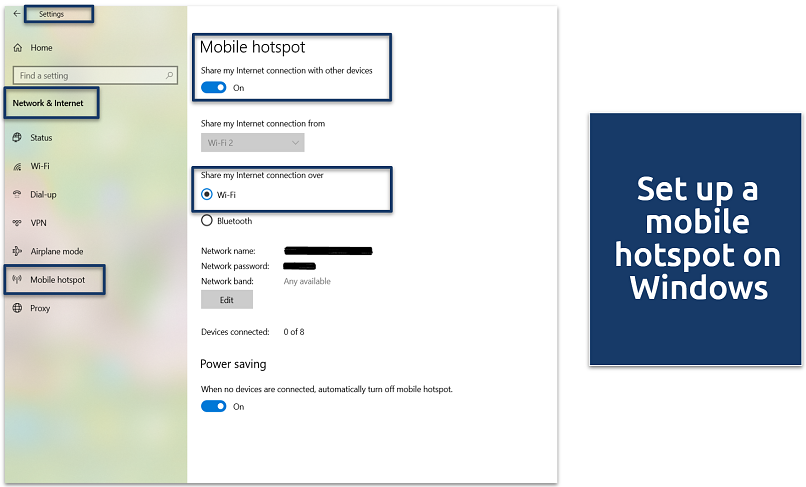 If you’re using WiFi, make sure the connection you want to share is active
If you’re using WiFi, make sure the connection you want to share is active - Click Edit to customize the network name and password.
- Other devices can now connect using the network name and password you set in the previous step.
Mac
- Go to System Preferences (Settings) > Sharing. Enable Internet Sharing from the list on the left.
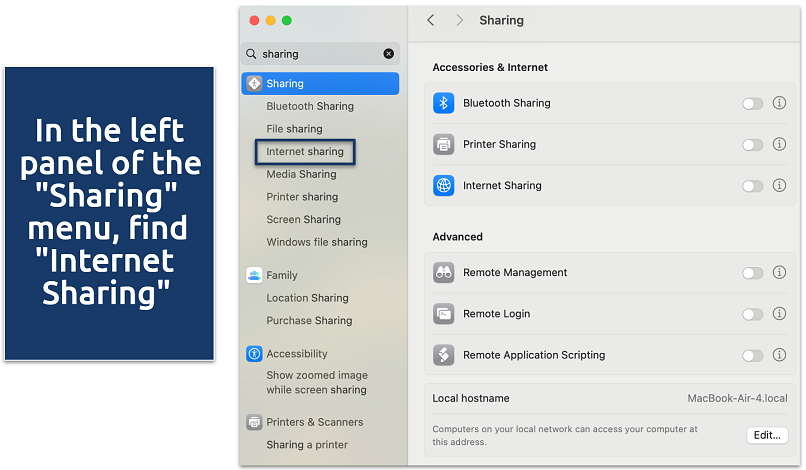 If the pop-up appears, click “Configure”
If the pop-up appears, click “Configure” - Choose the internet source and set the sharing method to WiFi.
- Set up the network name and password under WiFi Options, then check the box next to Internet Sharing to activate it.
2. How to Turn On a WiFi Hotspot on a Smartphone
Android
- Open Settings and go to Connections > Mobile Hotspot and Tethering (or a similar menu). Enable Mobile Hotspot and tap it to configure the network name, password, and security settings.
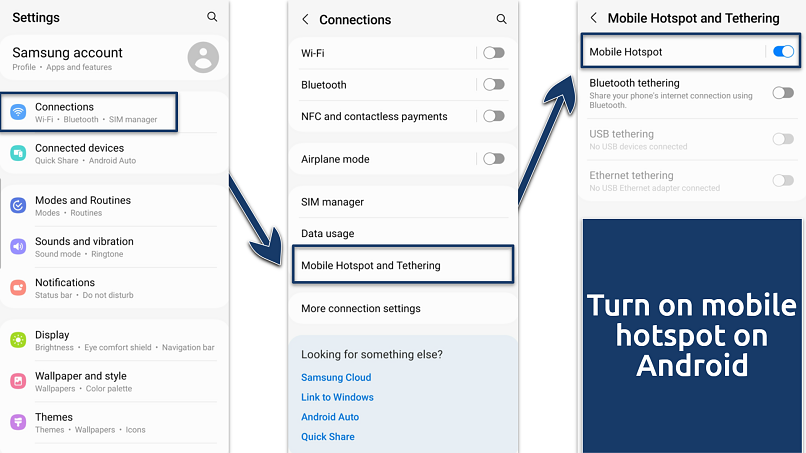 You may see a prompt about data and battery use — confirm to proceed
You may see a prompt about data and battery use — confirm to proceed - Other devices can now connect to your hotspot using the details you’ve set.
iPhone
- Go to Settings and navigate to Personal Hotspot (or Cellular > Personal Hotspot on some models).
- Toggle on Allow Others to Join to turn on the hotspot.
- Customize the WiFi password if needed. Nearby devices can now connect using your phone’s name as the SSID.
3. How to Turn On a WiFi Hotspot on a Portable Hotspot Device
- Power on the device.
- To activate the hotspot, follow the instructions in the user manual. Typically, this involves configuring the device through a web interface or app.
- Share the WiFi name (SSID) and password with the devices you want to connect.
Benefits of WiFi Hotspots
WiFi hotspots have become a vital part of our connected lives, providing a range of benefits that make staying online more convenient than ever. Here are some key advantages of using WiFi hotspots:
- Convenience anywhere. WiFi hotspots make it easy to access the internet wherever you are. Whether you’re at a café, in an airport, or relaxing at the park, hotspots allow you to stay connected without hassle. It’s like carrying your own internet connection with you.
- Save data, save money. WiFi hotspots help you avoid high mobile data usage. By connecting to a hotspot, you can browse, stream, and download without worrying about exceeding your data limit. This helps you save both your data and your money.
- Faster speeds. WiFi hotspots generally offer faster internet speeds than mobile data. This means quicker downloads, smoother streaming, and better browsing. For tasks like downloading large files or joining video calls, a WiFi hotspot is often your best option.
- Work from anywhere. For remote workers and digital nomads, WiFi hotspots are invaluable. They allow you to turn any location into an office, providing the flexibility to work from anywhere. Whether you’re answering emails, attending meetings, or collaborating on projects, thanks to hotspots, you’re always connected.
- Stay connected socially. WiFi hotspots make it easier to stay in touch with friends and family. You can keep up with social media, share updates in real time, and never miss an important message, no matter where you are.
- Entertainment on the go. Long waits are much easier to handle with a WiFi hotspot. Stream your favorite shows, play online games, or catch up on podcasts — all without using up your mobile data. It’s like having a portable entertainment hub in your pocket.
- Secure and private connections. While public WiFi networks can pose security risks, many hotspots — especially personal ones — offer more secure connections. This gives you greater peace of mind, knowing your sensitive information is better protected.
Risks and Security Concerns of Public WiFi Hotspots
While WiFi hotspots offer convenience, they also come with security risks that can put your data and devices at risk if you’re not careful. Public WiFi networks are particularly vulnerable to cyber threats, such as man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. In these attacks, hackers intercept the data exchanged between your device and the internet, stealing sensitive information like passwords, financial details, or personal files.
Another serious threat is fake WiFi hotspots, often referred to as “evil twin” networks. These are malicious networks created by hackers to look like legitimate public WiFi connections. When you unknowingly connect to one of these rogue networks, your device could become infected with malware. These deceptive hotspots are commonly found in busy public places, making it difficult to tell them apart from safe, legitimate connections.
How to Stay Safe When Using WiFi Hotspots
Staying safe on WiFi hotspots requires proactive steps to protect your data and devices:
- Use a VPN. This is one of the most effective ways to protect your data on public WiFi. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it much harder for snoops to intercept and read your data.
- Stick to HTTPS websites. Accessing websites that use HTTPS encryption adds an extra layer of security. This is particularly important when dealing with sensitive information like banking details or personal data.
- Turn on a firewall. Turning on your device’s firewall is a crucial step in protecting your connection on public WiFi. It acts as a barrier against unauthorized access to your system.
- Avoid automatic connections. Turning off automatic connections to open networks is an important security measure. This prevents your device from connecting to potentially malicious networks without your knowledge.
- Turn off file sharing. When using public WiFi, it’s advisable to turn off file sharing to prevent unauthorized access to your files.
- Keep software updated. Ensuring your operating system and applications are up-to-date is crucial for protecting against known vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords and encryption. For personal hotspots, using strong, unique passwords and enabling WPA2 or WPA3 encryption (where available) significantly enhances security.
How to Find a Secure WiFi Hotspot
Start by looking for networks from trusted places like reputable businesses or your internet service provider. ISP hotspots are often safer since they typically require authentication. Always double-check the network name (SSID) to make sure you’re connecting to the right one, not a fake.
Opt for networks with WPA3 or WPA2 encryption, which helps protect your data as it’s transmitted. Avoid networks that are “open” or don’t require a password, as these are more vulnerable to security risks.
For extra peace of mind, use apps like WiFi Map to find trusted hotspots. If you’re worried about public WiFi, consider using a personal mobile or portable hotspot to create a secure connection wherever you go.
What You Need to Know About Data Usage With WiFi Hotspots
Using a WiFi hotspot can quickly eat up your data, especially during activities that require a lot of bandwidth, like streaming or downloading large files. For example, streaming HD video can use between 1-3GB per hour, and video calls might consume up to 1GB per hour. To avoid unexpected charges or slower speeds, keep an eye on your data usage with tools available on your phone or hotspot device, and set up usage alerts.
Hotspots also drain your device’s battery, particularly when you connect multiple devices or use them in areas with weak signals. To save power, turn off the hotspot when you’re not using it, and consider carrying a portable charger for longer sessions.
If you’re using a Windows device, you can save data by setting your hotspot as a metered connection. Just go to Settings > Network & Internet > WiFi, select your network, and toggle on Set as a metered connection. This will pause automatic updates and prevent unnecessary data usage.
How WiFi Hotspots Compare to Other Wireless Technologies
Wireless technologies are constantly evolving, offering different ways to connect devices to the internet. Here’s a comparison of WiFi hotspots and other popular wireless technologies to highlight their unique purposes and capabilities:
| Technology | Alternate Names | Function |
| WiFi hotspots | Mobile hotspots, portable hotspots | Provide internet access by sharing a cellular data connection through WiFi — ideal for on-the-go connectivity |
| WLAN | Wireless local area network, wireless LAN | Allows communication between devices within a limited area (e.g., homes, offices) using WiFi |
| WiMAX | Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access | A wireless broadband technology, once seen as a WiFi alternative (now largely obsolete) |
| 5G | 5th generation mobile network | Offers ultra-fast data rates and low latency. Supports advanced mobile and IoT applications |
| Bluetooth | Short-range wireless communication | Facilitates quick, low-power device connections for tasks like file sharing or tethering |
| Satellite internet | N/A | Provides internet in remote areas using satellite signals, often slower and more expensive |
| Li-Fi | Light fidelity | Uses light to transmit data, offering high speeds but limited to line-of-sight environments |
FAQs on WiFi Hotspots
Can I use a mobile hotspot for gaming, streaming, or video calls?
You can use a mobile hotspot for gaming, streaming, or video calls if you have a strong network and sufficient data. These activities require fast speeds and low latency and consume significant amounts of data, so tracking your usage is crucial to prevent extra charges or reduced speeds. To avoid battery drain, keep your device plugged in or use a dedicated hotspot device for improved performance and extended battery life.
What is a WiFi hotspot in a car?
A WiFi hotspot in a car turns your vehicle into a mobile internet zone, allowing passengers to connect their devices while driving. Powered by the car’s cellular connection, it uses built-in hardware or an add-on device to create a wireless network. This is perfect for streaming, working, or keeping kids entertained during road trips, offering ease and connectivity no matter where the road takes you.
What should I do if my device says “connected to hotspot, no internet”?
To fix this, make sure your mobile hotspot is turned on so it can share the connection properly. If your device says connected to hotspot, no internet, it’s often due to a network conflict or settings issue. For mobile hotspots, you may see a message like While using Mobile Hotspot, WiFi is disabled. This means your device can’t connect to WiFi while it’s sharing its mobile data.
Try turning off the hotspot, reconnecting to the WiFi network, or checking that your cellular data is active and has a good signal. For public or portable hotspots, restarting both the hotspot and your device can help refresh the connection. If the issue persists, contact your hotspot provider for more support.
How fast are WiFi hotspots?
The speed of mobile WiFi hotspots depend on the cellular network used. Its performance is directly influenced by the strength and quality of the cellular service in the area. A 4G LTE hotspot typically delivers speeds of 20-30Mbps, which is great for browsing, streaming, and video calls. With 5G, speeds can soar beyond 1,000Mbps, offering lightning-fast performance for gaming, HD streaming, or working remotely. Public WiFi hotspots depend on the ISP plan used, and can also vary wildly in speed.
Your speed may also vary based on factors like your location, network congestion, and signal strength. For the best experience, use a hotspot in areas with strong cellular coverage or premium public WiFi plans.
Can I get unlimited hotspot data?
Yes, many carriers offer unlimited hotspot data plans, but there’s usually a catch. While the data may be “unlimited,” most plans have a high-speed data cap. Once you hit that limit, your speeds might be reduced, making activities like streaming difficult.
To avoid surprises, review your carrier’s terms carefully and consider plans with higher caps if you’re a heavy hotspot user. Expect to pay a premium price for truly unlimited high-speed data.
What is the optimal distance of a WiFi hotspot?
The optimal distance for a WiFi hotspot depends on the device and environment. Most hotspots only work best within 10-15m while indoors, where walls and furniture can weaken the signal. Outdoors, the range can extend up to 30-45m in open spaces.
For the strongest connection, stay as close to the hotspot as possible and avoid obstacles like walls or electronic interference. If the signal weakens, reposition the hotspot or move closer to it to improve performance.
Is using a WiFi hotspot free?
Using a WiFi hotspot isn’t always free — it depends on the type of hotspot. Public hotspots in cafes or airports are often free but may come with slower speeds or ads. Mobile hotspots, whether from your phone or a dedicated device, rely on your cellular data plan, which typically isn’t free and may include limits or extra charges. Always check for costs or data usage terms before connecting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, WiFi hotspots are versatile and essential tools for staying connected on the go. Whether you’re using a mobile hotspot, a public WiFi network, or a personal hotspot device, they all allow you to access the internet wirelessly and conveniently. Understanding how these hotspots work — by connecting to cellular networks or local networks — can help you make informed decisions about your internet needs.
Just remember to prioritize security when using public hotspots to protect your data. With the proper precautions, WiFi hotspots can be a powerful and reliable way to stay connected, no matter where you are.
React to this headline: